Deadly Animals You’ll Be Glad To Know Are Extinct

June 8, 2023
•21 min read
Here are some dangerous prehistoric animals you'll be glad to know are extinct!
The world’s full of some terrifying creatures who’d have no trouble making a quick meal out of us humans! But as scary some animals today may seem, there once existed even bigger, badder, and way more terrifying beasts. From child-eating eagles to colossal carnivorous whales, here are some deadly beasts that you’ll be glad to know are extinct.
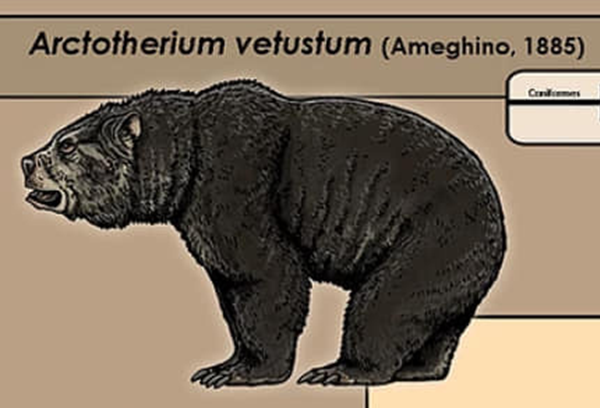
Arctotherium Angustidens
Stumbling across a grizzly bear is enough to make most people flee in fear. But even full-grown grizzlies look as harmless as cubs when compared to the Arctotherium Angustidens.
More commonly known as The Giant Short-Faced Bear, it hailed from South America and lived around 2.5 million years ago. With an average weight of 2 tons, Arctotherium Angustidens takes the title for Biggest Bear to Have Ever Lived! For some context, polar bears, the largest land carnivore alive today, are less than half the weight of these ancient bears. On top of that, these guys could reach an intimidating 14 feet when stood upright, that’s higher than a one-story building!Arctotherium vetustum basicamente ninguém estuda direito infelizmente, possui achados na Argentina e supostamente me Minas Gerais (até meu trabalho) Arte de PaleoZooBr
Haast’s Eagle
Fortunately, those bulky bears went extinct around 400,000 years before us Homo Sapiens first appeared. However, some long-extinct animals once did go toe-to-toe with man. Or technically, toe-to-claw, if the large skeletal remains of the carnivorous Haast’s Eagle are anything to go by!
These particular remains were found in the South Island of New Zealand. With a wingspan of up to 10 ft, the remains are so large that the bird is now considered to be the biggest eagle ever! The skeleton indicated it would have stood around half the height of an average man, and weighed in at some 40 pounds, four times that of a bald eagle!
Josephoartigasia Monesi
New York is famous for its massive rats, with some reaching the size of small dogs and house cats! But as big as a New York rat may be, their ancient cousins were something else. Introducing, the Josephoartigasia Monesi, who lived way back between 4 to 2 million years ago.
Considered to be the largest rodent to ever walk the face of the earth, these South American horrors measure in up to 10 feet long and weighed a whopping 2,200 pounds. For some perspective, that’s around the same weight as 12 adult humans! Size isn’t the only thing to watch out for with these mega-rats, though. They also bared horrifying incisors, reaching almost an entire foot long!#FossilFriday 🇺🇾Skull of Josephoartigasia monesi, the world's largest #rodent . 🐁 This dinomyid ("terrible mouse") from the Pliocene of #Uruguay had head like that of a small horse! 🐴Closest relative is the enigmatic #pacarana ; #chinchillas are cousins. animaldiversity.org/accounts/Dinom…

Megalania
About 2.5 million years ago, the dusty plains of Australia were home to some real terrors, but none could compete with the giant monitor lizard, known as Megalania.
Looking like a hulked-out version of a Komodo dragon, these prehistoric predators could reach a whopping 23 feet long, making them more than twice the size of their Komodo descendants. And, like Komodo dragons, Megalania are believed to have harbored venomous glands inside their jaw, that produced hemotoxin.
Thylacoleo Carnifex
Australia’s prehistoric horrors don’t end with Megalania! The Thylacoleo Carnifex, is an extinct marsupial lion that dominated the Australian wilderness between 2 million and 46,000 years ago.
Fossil evidence shows this wombat-lion hybrid measured in at around 5 feet long, about 2 ½ feet tall, and weighed around 220 pounds. This means that at their largest they were about the same weight as a modern jaguar, but slightly stockier! However, unlike jaguars, Thylacoleo carnifex weren’t equipped with sharp canine teeth. Instead, these monstrous marsupials had two pairs of giant incisors that they used to stab and pierce the flesh of their prey.
Gigantopithecus Blacki
Prehistoric primates, known as Gigantopithecus Blacki, that closely resemble bigfoot, roamed the forestland of Southern China roughly 2 million years ago. Exact size estimates are highly speculative because only teeth and jawbones have been discovered.
But even the existing evidence is enough to estimate that they stood around 10 feet tall and weighed up to 1,200 pounds, making them about twice as tall and nearly three times as heavy as silverback gorillas! Being located in Southern China, it’s likely that bamboo was a staple of its diet. Still, you wouldn’t mess with these things, considering that even a silverback gorilla is strong enough to pummel a human into mincemeat. But what caused such a big, broad beast to go extinct? It's mainly because it was too big and broad.
Daeodon
Pigs nowadays are mostly harmless but that has not always been the case. If we turn the clocks back 23 million years, Daeodon, or ‘dreadful pigs’, were wreaking havoc in North America.
This brute came in at a massive 1,650 pounds, stood nearly 6 feet tall at the shoulder, and was 10 feet long, giving it a rhino-like build. However, unlike rhinos, these guys didn’t stick to eating vegetation. If you look at their skull, their forward-facing eye sockets are designed to keep track of the prey they’re chasing. These pigs were predators! Recent research suggests that due to their lack of claws, they took down their prey by running alongside it, before ramming into it with brute force. To make matters more disturbing, these powerful piggys also came with canines that were some 10 inches long, designed for ripping flesh to pieces! Scientists believe that Daeodon eventually went extinct around 20 million years ago, due to increased global temperatures, depleting both vegetation and prey animals.Spinosaurus
If you mix a crocodile with a T-Rex it’d probably look like a Spinosaurus. Reaching lengths up to 59 feet and weighing a colossal 22 tons, this bulky beast is considered to be the largest carnivorous dinosaur to have ever walked the earth.
But their meal preference wasn’t usually terrestrial animals. Researchers believe that these dinos, hailing from North Africa, were water dwellers that mainly snacked on a feast of fishy food, including giant coelacanths, sawfish, and lungfish.Purussaurus
Crocs may look daunting enough as it is, but they’re nothing compared to the Purussaurus. This ravenous river giant once measured in at a head-spinning 35 feet long. That’s the same size as a school bus, and it was twice as long as a saltwater crocodile!
Unsurprisingly, it needed to eat a lot. Purussaurus went through roughly 90 pounds of food daily, twenty times the requirement for the modern American alligator! And, if you’re wondering what exactly Purussaurus ate, the simple answer is anything. From car-sized Stupendemys turtles to giant ground sloths, the world was their buffet.
Utahraptor
If you’ve seen Jurassic Park, you’ll know just how scary Velociraptors once were! But they’re actually the smaller cousin of Utahraptors. These bird-like dinosaurs date back 125 million years, and stood up to 18 feet long, making them the length of a standard shipping container, but with a killer instinct!
To help with that killing, they came armed with a 15-inch claw on each foot. Just one kick from this bad boy was capable of slicing through an animal and it wouldn't be an easy task to run from these guys. Based on their slender legs and the speed of dinosaurs of similar sizes, it’s believed that Utahraptors could run up to 30 miles per hour!Smilodon
Diego, the Sabretooth cat from the endless series of Ice Age movies, may look cuddly on screen, but trying to snuggle up to a real Sabretooth cat would have left you with some serious scars!
Smilodon, the most famous of the Sabretooth cat species, lived in the Americas some 2.5 million years ago. The 8-inch, fang-like teeth sticking out these big cat’s mouths look utterly terrifying, but these upper canines aren’t believed to have packed much of a punch. Computer scans of the fossilized skulls of sabretooth cats revealed that they generated a biteforce of just 220 pounds, which is only slightly stronger than a human bite. To make up for this, the Smilodon had proportionally longer front legs and a much more muscular build, compared to big cats today. This would’ve helped them wrestle prey to the ground WWE style, before pinning their head down and making a precise bite to the throat with their curved canines. But ferocious fangs couldn’t save the Smilodon from the effects of climate change and humans, who overhunted the cat’s prey, eventually leading to its extinction 10,000 years ago.
Megapiranha
Walking on prehistoric land would have been scary, but swimming in the rivers would have been way worse! Around 8-10 million years ago in the Late Miocene, you would’ve had the horror of coming across Megapiranha in the rivers of South America.
And, as the name suggests, these famously carnivorous fish were huge. They grew to an alarming 28 inches, over 2 ft long, more than double the size of modern piranhas! They weighed around 22 pounds, making them 4 times heavier than the existing feisty fish! But size isn’t the only thing that made these fish scary. Based off the bite force of living black piranhas, scientists estimate that the Megapiranha would’ve chomped down with a staggering force of 1,000 pounds of force. That would give its bite the same whack of that of a small great white shark, despite the fanged fish only weighing one fortieth of a great white.
Cameroceras
We know that wading in prehistoric waters would have been a bad idea, but it can always get worse, thanks to the ancient, alien-looking Cameroceras!
Cameroceras lived during the Ordovician period, some 470 million years ago and was an early cephalopod; a type of mollusk classification that includes the more familiar octopus, squid and cuttlefish. The eye-catching feature of this quirky character was its immense 36-foot-long shell, used to protect the Cameroceras main body.
Megatherium Americanum
Sloths might be pretty small and cute but, astonishingly, their ancestor Megatherium Americanum is the opposite of them in almost every way. These giant sloths wandered through South America between 400,000 and 8,000 years ago.
They stood at an imposing 12 feet tall, and weighed in at a hefty 4 tons, around the same weight as an elephant. And, if that wasn’t bizarre enough, it’s likely that Megatheriums were hairless to prevent them from overheating. To make matters even worse, they came with 7-inch claws. But scientists don’t believe that Megatherium were carnivorous; instead, it’s likely that their claws would’ve been used to swipe down tall vegetation. While it’s currently not clear whether their diet included some meat, it is possible that they occasionally scavenged off carcasses. Some theories go even further, speculating that Megatherium would actively hunt smaller herbivores by flipping them over and slashing them open with its claws.
Therizinosaurus
The ground sloth may have had some long claws, but those are nothing compared to what the Therizinosaurus sported. The scythe lizard, as it was known, lived in Asia some 70 million years ago and could grow to a gangly 16 feet tall.
But the most terrifying thing about the Therizinosaurus wasn’t its height, but its lengthy claws. These bad boys stretched over one and a half feet long, making them the longest claws of any animal ever! When these guys weren’t impersonating Edward Scissorhands, they were using their lengthy appendages to pull vegetation within reach. Despite their crazy claws, it's believed that they were strictly herbivores, though someone forgot to tell that to the makers of Jurassic World: Dominion. This is down to their bipedal stance which, similar to other herbivores of the time, helped them reach further up into trees. Even still, you wouldn’t want to get into a fight with one of these things flailing their death claws at you! Sadly, for them, the Therizinosaurus is believed to have perished in the K-T mass extinction event.Platybelodon
Some prehistoric animal ancestors look pretty weird, and that’s definitely the case with the Platybelodon! This giant mammal lived in Asia, Africa and North America between 20 million and 8 million years ago. They’re a genus of larger herbivorous proboscidean mammals related to modern day elephants!

Quetzalcoatlus
The Quetzalcoatlus was a flying reptile which was alive some 70 million years ago. And, after learning about these winged nightmares, you'd wish they’d lived even further back in time. There aren’t many things more terrifying than the prospect of having a 16-foot-tall reptilian stork hunting you down.


Rhamphorhynchus
But the winged nightmares aren’t over! Another flapping fright is known as a Rhamphorhynchus, a flying reptile that soared the skies of Europe and Africa, between 154 and 137 million years ago.
Unlike the Quetzalcoatlus, these guys weren’t blessed with great size. Their wingspan was about 6 feet long, while their total body length was only 20 inches long, making them pigeon-sized, albeit with wider wings. But what they lacked in size, they more than make up for in terror, because the jaws of Rhamphorhynchus were filled with needle-like teeth. It may look like they lost a fight with a thorn bush, but these terrifying teeth served an important purpose. And that purpose was to help these ravenous reptiles catch fish by dip-feeding. When the Rhamphorhynchus saw its prey, it would swim just above the water and lower its spiky bill in, impaling and catching the super slippery fish in the process. And, with the prey skewered, the Rhamphorhynchus would’ve swallowed it down in one. If these guys ever miraculously come back from extinction, just remember to never hand feed them!Livyatan
We’ve taken a deep dive into some of the more terrifying things you can find in the water, but visually, very few are as terrifying as the Livyatan. This 55-foot-long genus of carnivorous sperm whale ruled the oceans off South America around 9 million years ago.

Megalodon
If you thought nothing could beat the might of the Livyatan, let me introduce you to the Megalodon, a species of mackerel shark that puts Jaws to shame. This 50-foot-long fish was over 3 times the length of a great white shark!
And these beefy boys were heavy too, weighing in at around 70 tons, which is equivalent to roughly 10 elephants! On top of that, their jaws could span over 6 feet wide, easily enough room for an entire human.